How to Find the Area of a Triangle: Formulas & Examples
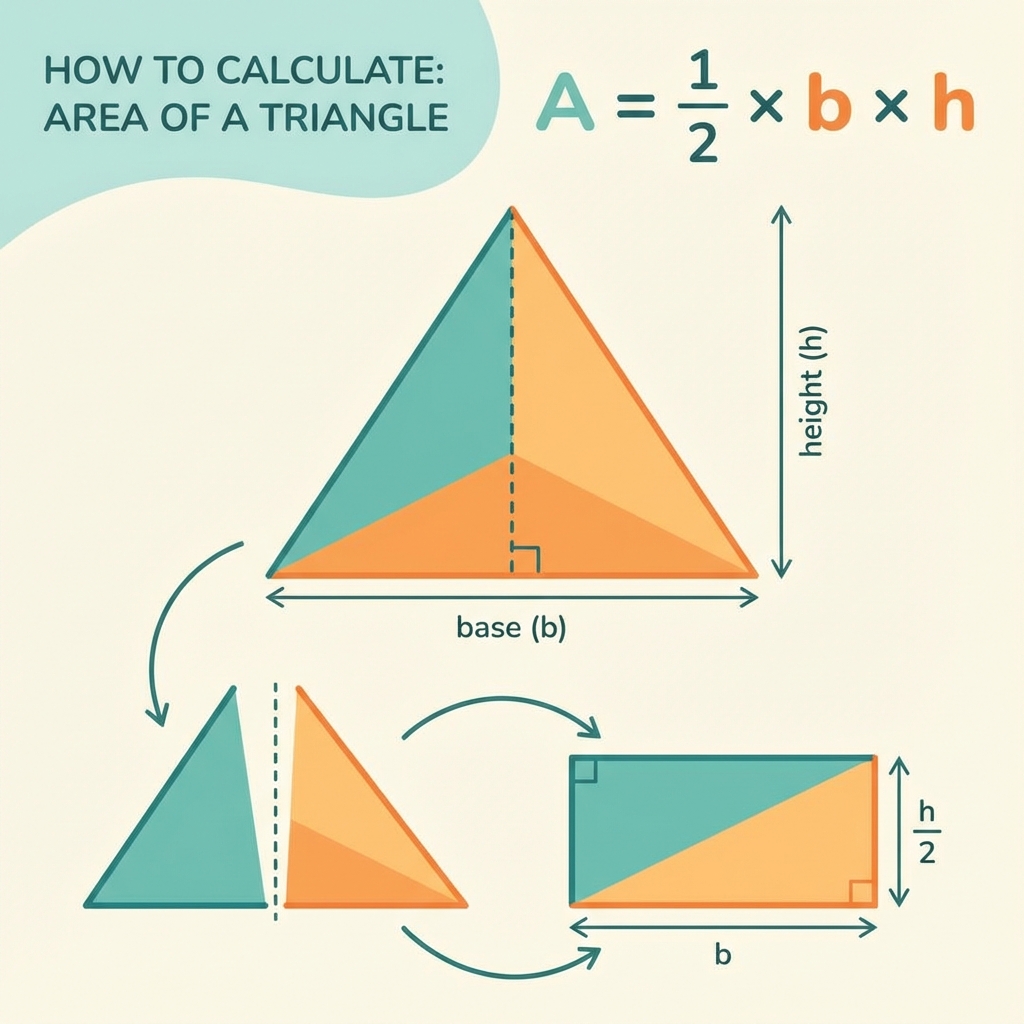
Calculating the area of a triangle is a fundamental skill in geometry. Whether you're a student working on homework or a professional in design or construction, knowing the right formula is essential. In this guide, we'll explore the most common methods to find the area of a triangle.
1. The Standard Formula (Base & Height)
The most widely used formula for the area of a triangle is based on its base and height.
Area = ½ × base × height
Where:
- Base (b): The length of the bottom side of the triangle.
- Height (h): The perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite vertex.
Example:
Find the area of a triangle with a base of 10 cm and a height of 6 cm.
Area = ½ × 10 × 6
Area = 5 × 6
Area = 30 cm²
2. Heron's Formula (Three Sides)
What if you know the lengths of all three sides but don't know the height? That's where Heron's Formula comes in. It allows you to calculate the area using only the side lengths (a, b, and c).
First, calculate the semi-perimeter (s):
Then, use the formula:
Area = √[s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)]
Example:
Find the area of a triangle with sides 3, 4, and 5.
- Calculate s: (3 + 4 + 5) / 2 = 12 / 2 = 6
- Apply formula: √[6(6-3)(6-4)(6-5)]
- Simplify: √[6(3)(2)(1)] = √36
- Area = 6
3. Area of a Right Triangle
For a right-angled triangle, the two sides that form the right angle can be treated as the base and height.
Formula: Area = (Leg 1 × Leg 2) / 2
4. Area of an Equilateral Triangle
If all three sides are equal (length 'a'), you can use a simplified formula:
Area = (√3 / 4) × a²
Conclusion
Understanding these formulas gives you the flexibility to solve any triangle area problem. For instant results without the manual math, use our free online tool.