Understanding Triangle Properties: Sides and Angles
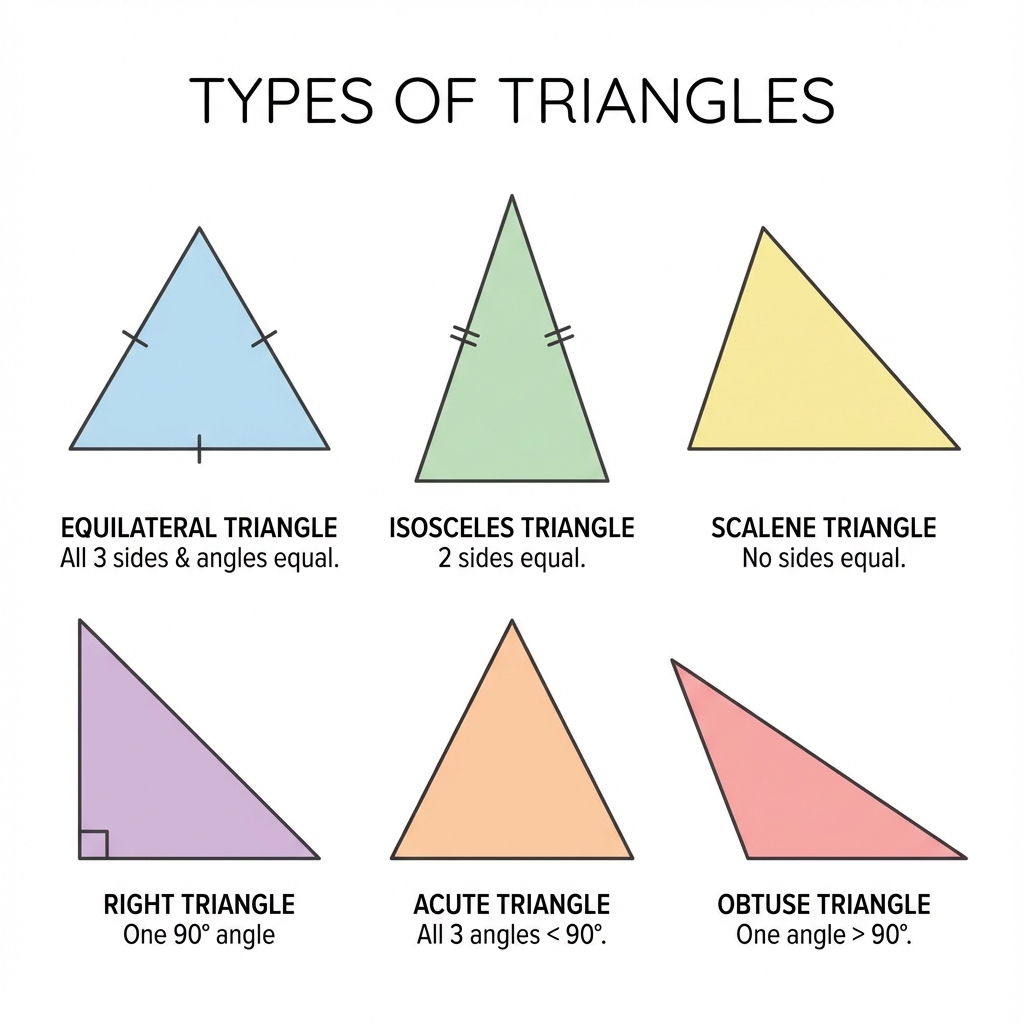
Triangles are one of the most basic yet fascinating shapes in geometry. Defined as a polygon with three edges and three vertices, they come in various forms. Understanding how to classify them is key to mastering geometry.
Classification by Sides
Triangles can be categorized based on the lengths of their sides:
- Equilateral Triangle: All three sides are equal in length. Consequently, all three internal angles are also equal (60° each).
- Isosceles Triangle: At least two sides are equal in length. The angles opposite these equal sides are also equal.
- Scalene Triangle: All three sides have different lengths. All three internal angles are also different.
Classification by Angles
We can also classify triangles based on their internal angles:
- Acute Triangle: All three angles are less than 90° (acute angles).
- Right Triangle: Has exactly one angle that is 90° (a right angle). The side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse.
- Obtuse Triangle: Has one angle that is greater than 90° (an obtuse angle).
Key Theorems
1. Angle Sum Property
The sum of the internal angles of any triangle in a Euclidean plane is always 180 degrees. This is a fundamental rule used to find missing angles.
2. Triangle Inequality Theorem
This theorem states that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the length of the third side. If this condition isn't met, the lines cannot connect to form a closed triangle.
3. Pythagorean Theorem
Specific to right-angled triangles, this famous theorem states:
a² + b² = c²
Where 'a' and 'b' are the legs and 'c' is the hypotenuse (longest side).
Explore More
Want to calculate properties of a specific triangle? Try our calculator to get instant answers for area, perimeter, and more.