LCM Calculator
Calculate the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of two or more numbers instantly. Also known as Lowest Common Multiple or Least Common Denominator (LCD).
Perfect for adding fractions, solving math problems, and finding common denominators. Get step-by-step solutions with detailed explanations.
Enter at least two positive integers separated by commas
Why Use Our LCM Calculator?
Instant Results
Get the LCM of any numbers in milliseconds. Supports two or more numbers with step-by-step solutions showing the calculation process.
100% Accurate
Uses the proven LCM = (a × b) / GCD formula for guaranteed accuracy. Perfect for homework, exams, and professional work.
Learn & Understand
See step-by-step calculations to understand how the LCM is computed. Great for learning and verifying your manual calculations.
What is LCM (Least Common Multiple)?
The Least Common Multiple (LCM), also called the Lowest Common Multiple or Least Common Denominator (LCD) when working with fractions, is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all given numbers without a remainder.
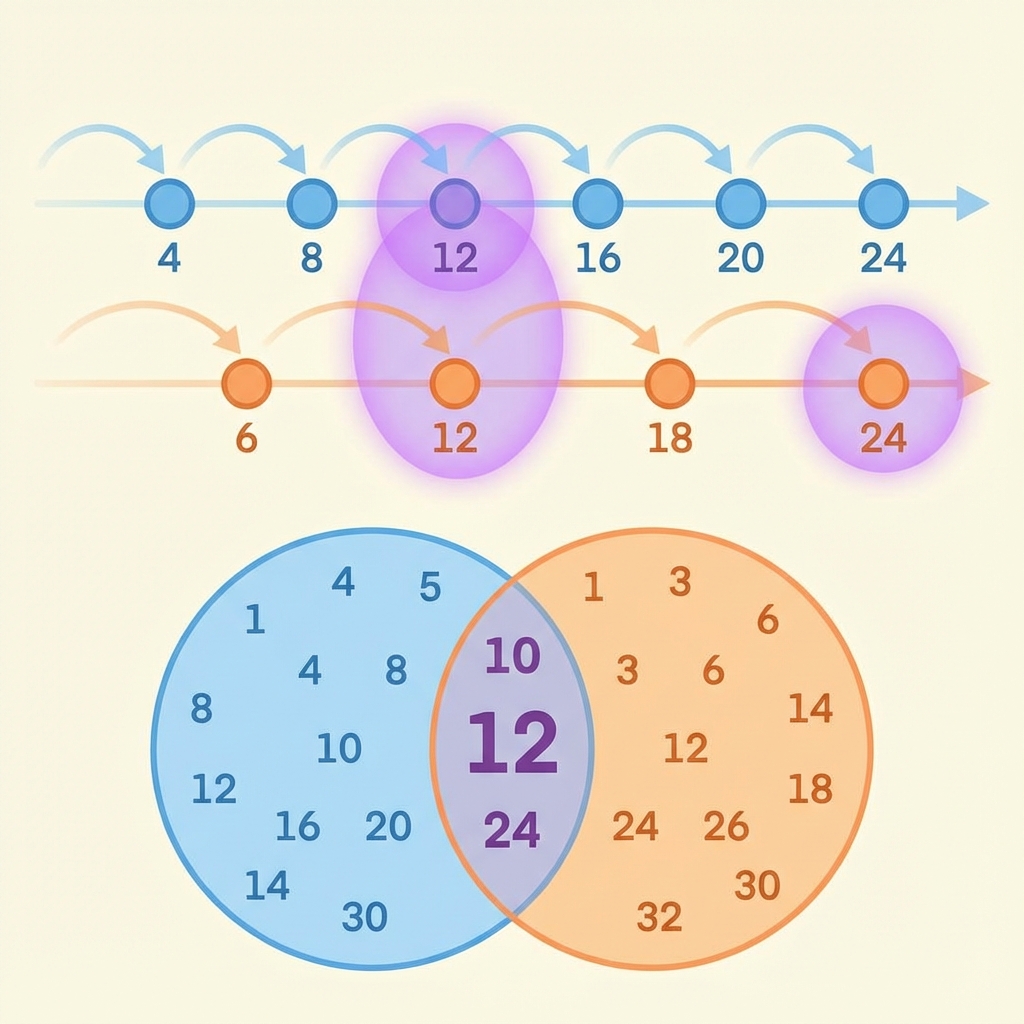
For example, consider the numbers 4 and 6:
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28...
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30...
- Common multiples: 12, 24, 36...
- Least Common Multiple: 12
The LCM is essential in mathematics for adding and subtracting fractions with different denominators, solving problems involving repeating events, and understanding number relationships.
How to Calculate LCM
Method 1: Listing Multiples (Small Numbers)
- List the multiples of each number
- Identify the common multiples
- Select the smallest common multiple
Example: LCM(4, 6)
Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24...
Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30...
Common: 12, 24, 36...
LCM = 12
Method 2: Using GCD Formula (Most Efficient)
Use the relationship: LCM(a, b) = (a × b) / GCD(a, b)
- Find the GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) of the numbers
- Multiply the two numbers together
- Divide the product by the GCD
Example: LCM(12, 18)
GCD(12, 18) = 6
LCM = (12 × 18) / 6
LCM = 216 / 6
LCM = 36
Method 3: Prime Factorization
- Find the prime factorization of each number
- Take the highest power of each prime factor
- Multiply these together
Example: LCM(12, 18)
12 = 2² × 3
18 = 2 × 3²
LCM = 2² × 3² = 4 × 9
LCM = 36
For Multiple Numbers
To find LCM of more than two numbers:
- Find LCM of the first two numbers
- Find LCM of that result with the third number
- Continue for all remaining numbers
Example: LCM(4, 6, 8)
LCM(4, 6) = 12
LCM(12, 8) = 24
LCM = 24
Common Uses for LCM
➗ Adding Fractions
Find the LCM of denominators to get a common denominator for adding or subtracting fractions. Essential for fraction arithmetic and simplification.
📚 Math Homework
Essential for algebra, number theory, and arithmetic problems. Verify your manual calculations and understand the step-by-step process.
⏰ Scheduling & Cycles
Determine when repeating events will coincide. For example, if event A repeats every 4 days and event B every 6 days, they'll coincide every LCM(4,6) = 12 days.
📐 Measurement & Design
Find common measurements for tiling, patterns, and modular designs. Calculate the smallest size that accommodates different module sizes.
🎵 Music Theory
Determine when different rhythmic patterns align. Find common measures for polyrhythms and complex time signatures.
🔢 Number Theory
Fundamental concept in mathematics used in modular arithmetic, solving Diophantine equations, and understanding number relationships.
Related Calculators
View AllRelated Articles
View All Articles
LCM Calculator: How to Find the Least Common Multiple Step by Step
Learn how to find the Least Common Multiple (LCM) with our step-by-step guide.
What Is the Least Common Multiple (LCM)? Definition, Examples, and Uses
Understand the concept of Least Common Multiple (LCM). Clear definitions and examples.
LCM vs GCD: Key Differences with Practical Examples
Confused between LCM and GCD? Learn the key differences and when to use each one.